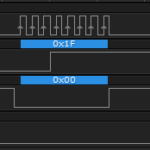
In previous sections, we’ve learned how to convert byte values from decimal to binary to hex and back again. Now we need to quickly cover the concepts behind bitwise and boolean operators, that will eventually allow us to modify the internal contents of a byte of data, and compare multiple values simultaneously.
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise Operators are used to modify the contents of data at the individual bit level. There are four primary bitwise operators, AND, OR, XOR and NOT, and they relate directly to their logic symbol equivalent truth tables. Their usage in code can be a little tricky though.
The symbol used to compare values using the AND operator is the ampersand: &
0 & 0 = 0
0 & 1 = 0
1 & 0 = 0
1 & 1 = 1
What would the value in binary be of B00000001 & B11101101…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of B11101101 & B10110111…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of 134 & 78…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
The symbol used to compare values using the OR operator is the pipe symbol: |
0 | 0 = 0
0 | 1 = 1
1 | 0 = 1
1 | 1 = 1
What would the value in binary be of B00000001 | B11101101…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of B11101101 | B10110111…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of 134 | 78…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
The symbol used to compare values using the XOR operator is the caret: ^
0 ^ 0 = 0
0 ^ 1 = 1
1 ^ 0 = 1
1 ^ 1 = 0
What would the value in binary be of B00000001 ^ B11101101…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of B11101101 ^ B10110111…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of 134 ^ 78…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
The symbol used to compare values using the NOT operator is the tilde: ~
~0 = 1
~1 = 0
What would the value in binary be of ~B11101101…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of ~B10110111…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
What would the value in binary be of ~134…
Hover Mouse Here For Answer
Boolean Operators
While the logic of the boolean operators AND, OR and NOT are exactly the same as their bitwise counterparts, they aren’t used to perform a modification of the underlying value, they are used to compare values and return either a boolean True or False, or join evaluations together.
The boolean operator AND has the symbol of a double ampersand, && and is used to join evaluations. Examples:
if (meal = now && meal = cookies) then Cookie Monster will be happy.
if (money > 0 && billCollectors = 0) then you're happy.
The boolean operator OR has the symbol of a double pipe, || and is used to join evaluations. Examples:
if (drink = kölsch || drink = singleMalt) then Dan will be happy.
if (parkingMeterTime > 0 || parkingTickets = 0) then you're happy.
The boolean operator NOT has the symbol of an exclamation point (commonly called a “bang”), ! and is used to test a value quickly. Examples:
if (!milkSpoiled) then cereal for breakfast
if (!workDay) then you're happy.